AFFILIATED COMPANIES

JSC Rustavi Azot
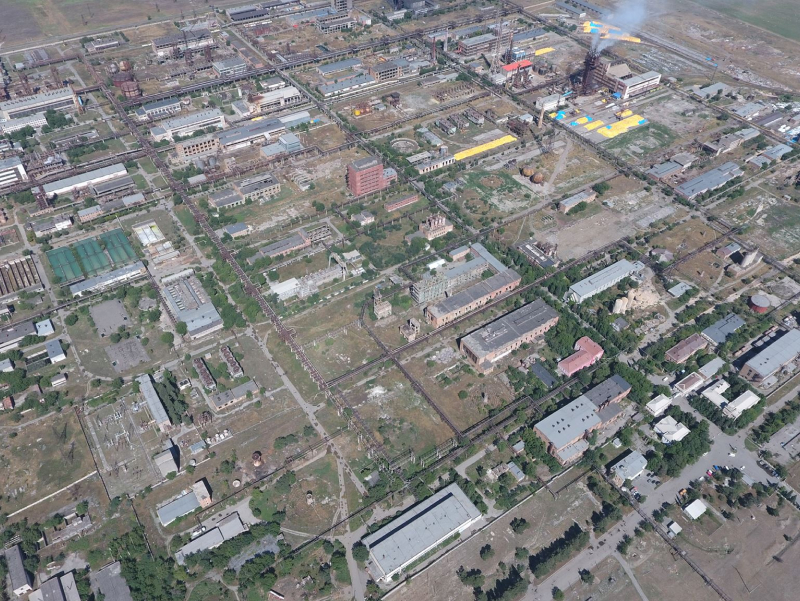
GeorgiaEstablished in 1956, JSC Rustavi Azot is one of the largest producers of fertilizers and industrial chemical products in the Caucasus region. JSC Rustavi Azot's key product is ammonium nitrate, predominantly used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer. The company also produces sodium cyanide, which is mainly used in gold leaching process.
Plant is located in Rustavi (Southeast of Georgia) and has excellent access to transport infrastructure to export its products via railway and Black Sea ports. JSC Rustavi Azot's sales are predominantly export-oriented.

JSC Rustavi Azot
Georgia| Production Capacity Ammonium Nitrate Sodium Cyanide |
550 KTA 15 KTA |
| Key Raw Materials | Natural gas |
| # of Employees | 2000 |
| Year started | 1956 |
| Year acquired | 2023 |

JSC Rustavi Azot
GeorgiaAmmonia Plant
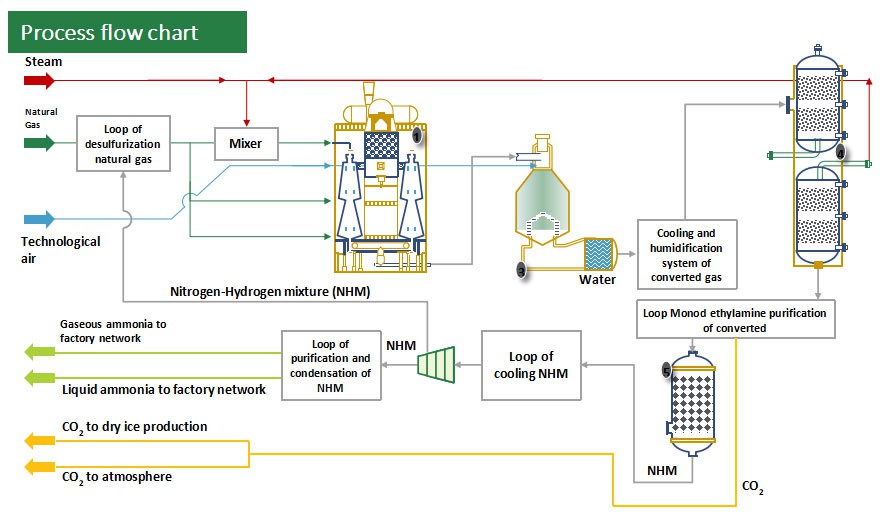
230 KTPA Ammonia Plant commissioned in 1980 based on GIAP technology. Rehabilitated in 2007.The Ammonia Plant is based on NG-Steam Reforming process designed by GIAP. The plant uses natural gas as the primary feedstock and fuel. Natural gas is first de-sulphurised and then steam reformed. The process stream is further subjected to secondary reforming with air. After a series of further steps, synth-gas, with a specific molar ratio of hydrogen to nitrogen, is made. The same is subsequently synthesized into Ammonia with the help of a catalyst. Carbon dioxide is formed during the process, which is separated and will be used in the future upcoming projects. Ammonia is used as an intermediate raw material for manufacturing Nitric Acid, Ammonium Nitrate and Sodium Cyanide.
Ammonium Nitrate Plant
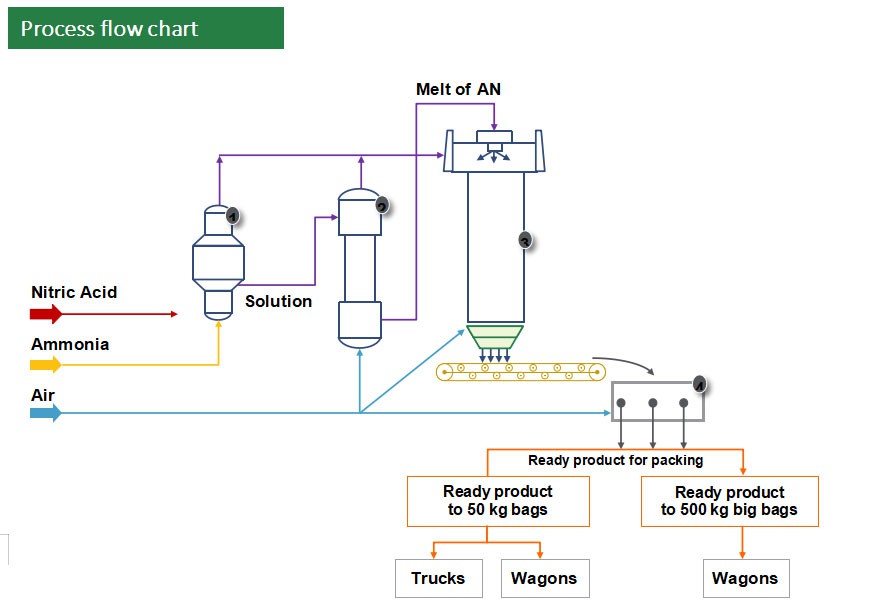
The Ammonium Nitrate plant has a capacity of 550 KTPA and was commissioned in 1979. The Ammonium Nitrate production process is based on Russian GIAP technology. Ammonium Nitrate is produced by neutralization of nitric acid by gaseous ammonia, that is further granulated. Main nutrient element in AN is nitrogen with 34.4% nitric concentration.
Sodium Cyanide plant
The Sodium Cyanide plant capacity of 15 KTPA was commissioned in 1966. Sodium Cyanide production process is of Russian Technology GIAP, based on joint cooperation with Japanese technology providers Nisso Engineering and Kiokho Tsusho Kaita. Cyanic Acid is derived from the oxidation of Ammonia and natural gas. The derived Cyanic Acid is neutralised with Caustic Soda, and the result is Sodium Cyanide solution which is further steam dried, crystalised through centrifugal method and finally bracketed.








